Product Life Cycle Stages
Product Life Cycle (PLC) is a term to describe individual stages in the life of a product or service and is often used in product development business planning. Business priorities, budgeting, funding, production, distribution marketing – all these factors change depending on how long a product or service has been in the market. The four distinct stages affect sales and profitability of a product.
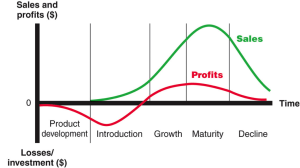
Introduction:
The introduction stage is when the new product is launched. It’s typically the riskiest stage because of the uncertainty of how the market will respond. It typically takes time (unless a technology-related product or service), experiences slow sales growth with little or no profit. Marketing and distribution costs are high as the company tries to gain initial distribution and increase awareness.
Growth:
A product reaches the growth stage with the new product satisfies the market. Sales and distribution increase, and so does the competition. A company reaches price stability or may decrease price to increase volume. Profits increase while manufacturing and promotion costs gain economies of scale. A company will often introduce secondary products or new features to the product to maintain product differentiation as competition intensifies.
Maturity:
The maturity stage is often the longest-lasting stage of a product that has gained consumer acceptance. The market is filled with many suppliers and substitute products. This overcapacity leads to competition, which leads to lower profit margins. There is minimal growth potential for the product, so the ability to convert new customers to your product is a major challenge.
Decline:
In the decline stage, the market is saturated and sales and profits decline. The competition is taking over the company’s market share and the company becomes cost conscious. Three options are left: 1) reposition or rebrand the product; 2) maintain the product as is and reduce costs to get maximum profit; and 3) remove the product from the market.
